Improving Reasoning with Contrastive Visual Information for Visual Question Answering
Yu Long, Pengjie Tang, Hanli Wang and Jian Yu
Overview:
Visual Question Answering (VQA) aims to output a correct answerbased on cross-modality inputs including question and visual content. Ingeneral pipeline, information reasoning plays the key role for a reasonableanswer. However, visual information is commonly not fully employed inmany popular models nowadays. Facing this challenge, a new strategyis proposed in this work to make the best of visual information duringreasoning. In detail, visual information is divided into two subsets:(1) question-relevant visual set, and (2) question-irrelevant visual set.Then, both of these two sets are employed by reasoning to generatereasonable outputs. Experiments are conducted on the benchmark VQAv2dataset, which demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed strategy.
Method:
The framework of the proposed method is shown in Fig. 1, including the feature extraction stage, coarse reasoning stage and fine-grained reasoning stage. First, the features of both image and question are extracted by Faster R-CNN and RNN/BERT respectively. Then, these features are sent into a coarse reasoning model, which could coarsely fuse these two features and split the image feature into two parts. Next, a two-branch reasoning module is proposed which is established based on the existing model(i.e., BLOCK, LXMERT etc), and the image features are sent into the corresponding branch of this module with the question feature. At last, the outputs of these two branches are used to calculate loss function, in which two new loss functions are proposed for the new branch (the details of the proposed method can be seen in the paper).
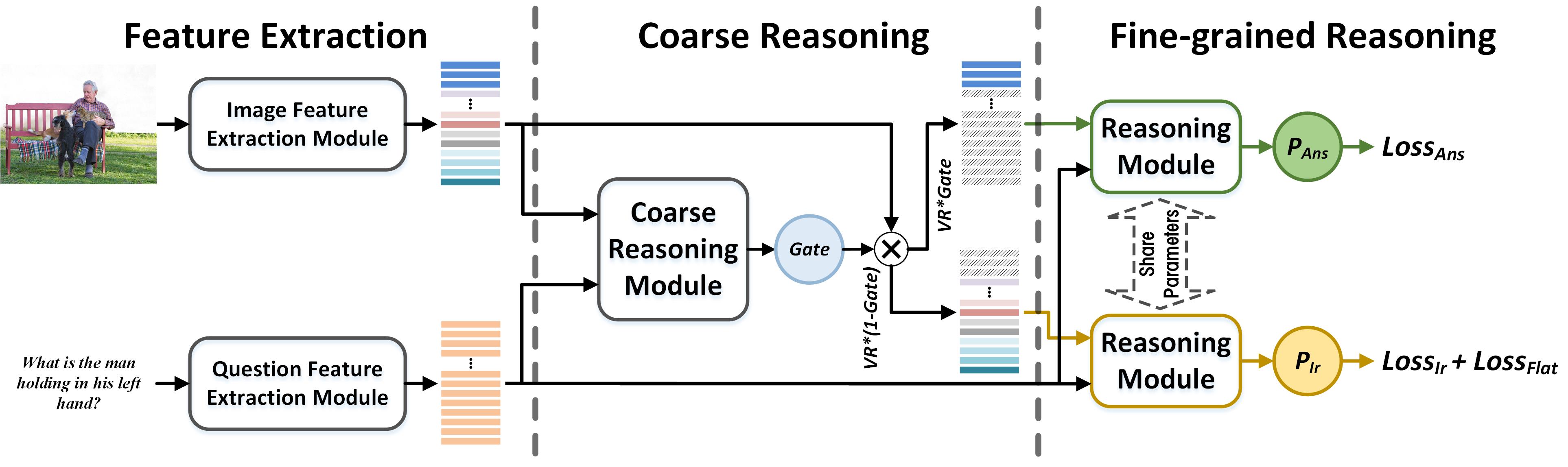
Fig. 1 Overview of the proposed framework for VQA.
Results:
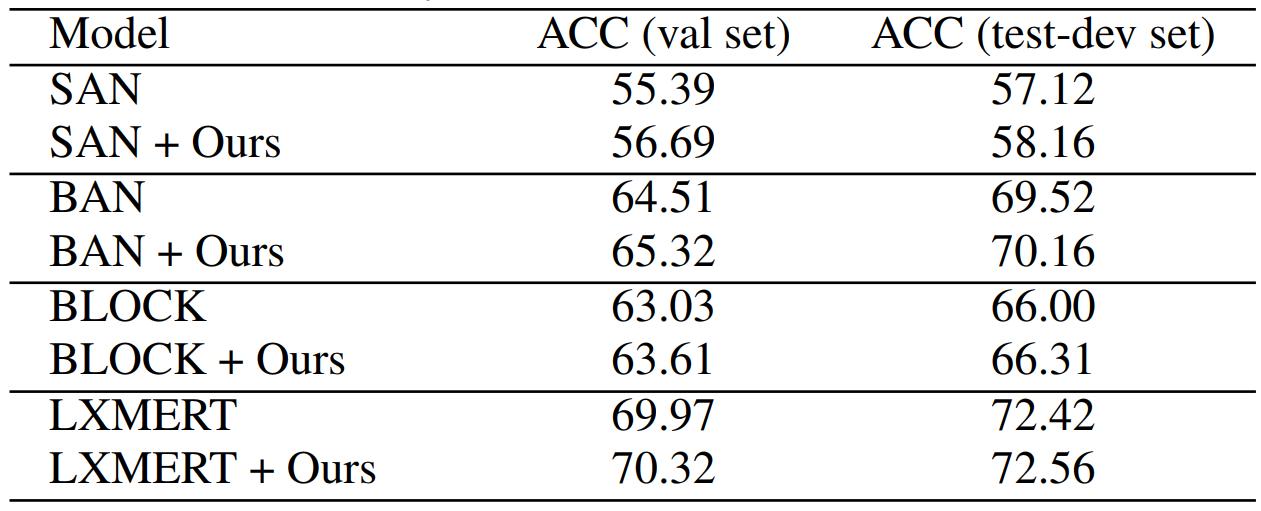
The proposed method is deployed on the baseline modelsof SAN, BAN, BLOCK and LXMERT, and the dataset used in this work is VQAv2. The results are shown in Table 1. The performances of these models are evaluated by Accuracy(%), which indicate that the proposed method can help the baseline models to get better performances.
Table 1 Performance (%) of the proposed strategy on the VQAv2 dataset,“ACC (val set)” means the accuracy on the val set and “ACC (test-dev set)”means the accuracy on the test-dev set.
By contrast, the model using the proposed strategy performs worsethan the backbone without using proper visual input, as seen from theresults in Table 2. Concretely, the visual information is changed in thevalidation stage, and “WV” means each image in the dataset is changedby another image, while “ZV” means each image is replaced by a zeromatrix. The performance trend is consistent with the intuition that the newdesigned branch can make the model to grab more correlations betweenvisual information and question and ignore the correlation between the input question and the output label.
Table 2 Performance (%) of the proposed strategy with different visual inputs on the VQAv2 dataset.
![]()
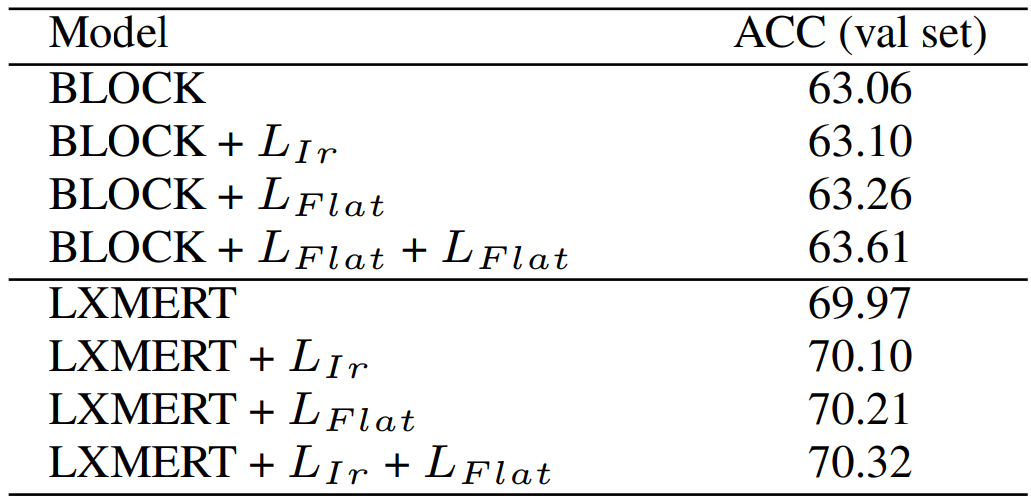
In addition to the above experiments, two ablation experiments concerning more parameters and loss functions are conducted. As shown in Table 3 and Table 4, The main effectiveness of the proposed methods gains from proper loss functions.
Table 3 Performance (%) comparison of several backbone models with/without CRM on the VQAv2 val set.
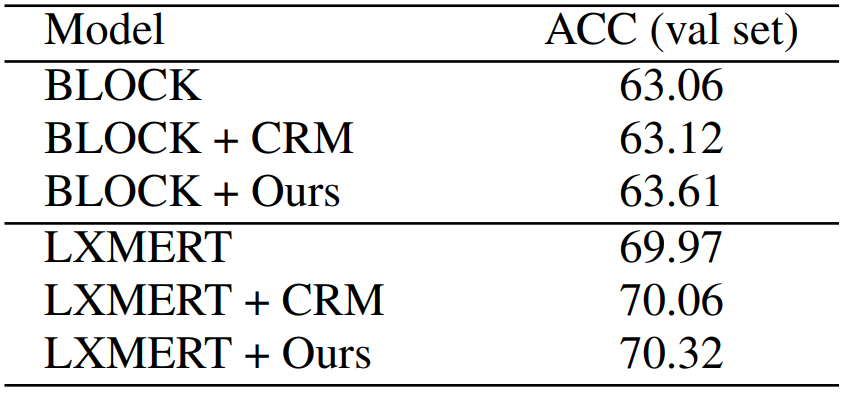
Table 4 Performance (%) comparison of several backbone models with different loss functions on the VQAv2 val set.
Source Code:
Citation:
Please cite the following paper if you use the code or feel it useful:
Yu Long, Pengjie Tang, Hanli Wang, and Jian Yu, Improving Reasoning with Contrastive VisualInformation for Visual Question Answering, Electronics Letters, accepted, 2021.
