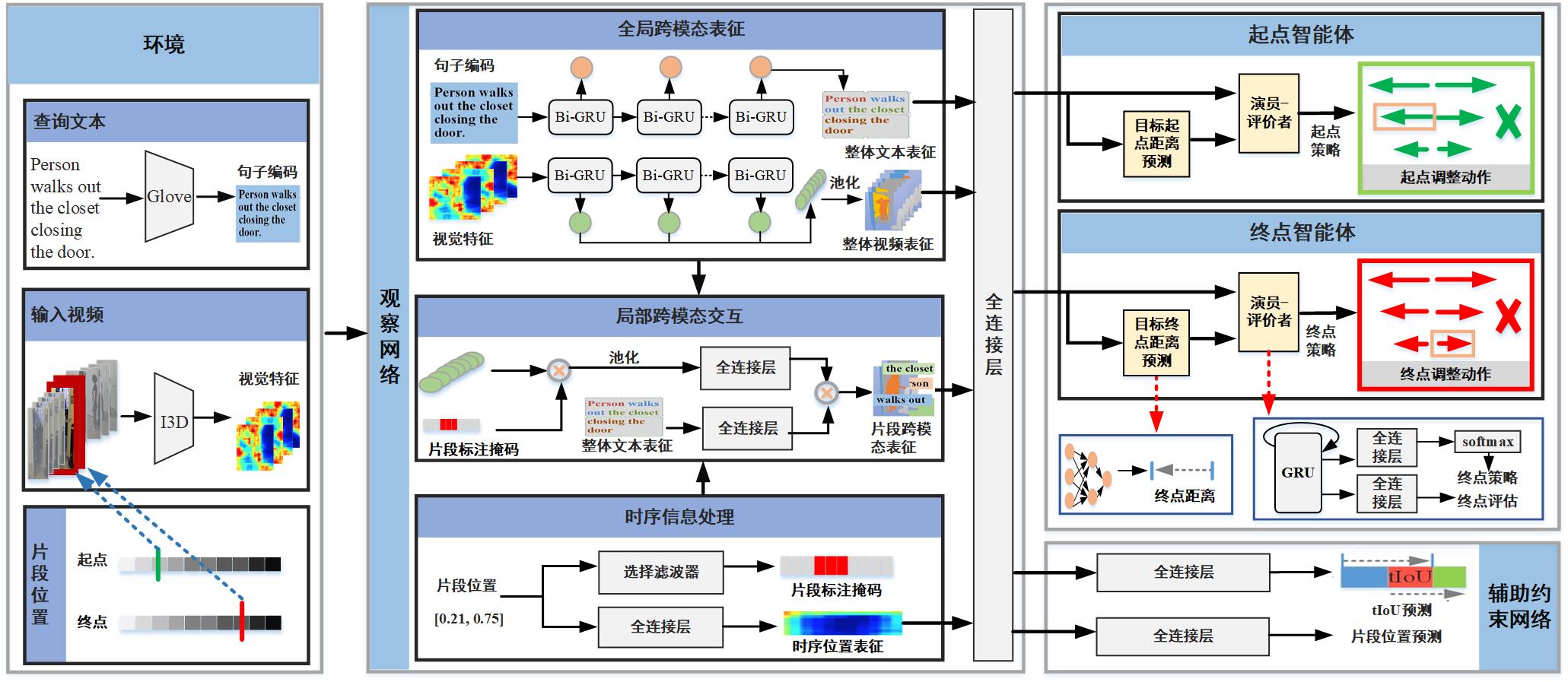
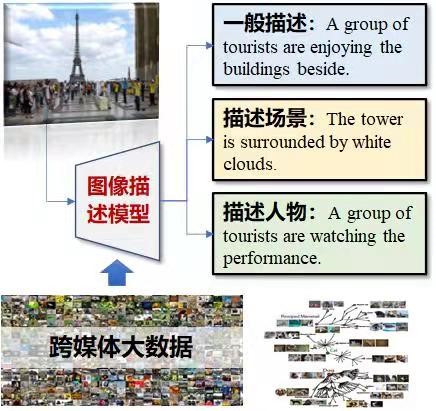
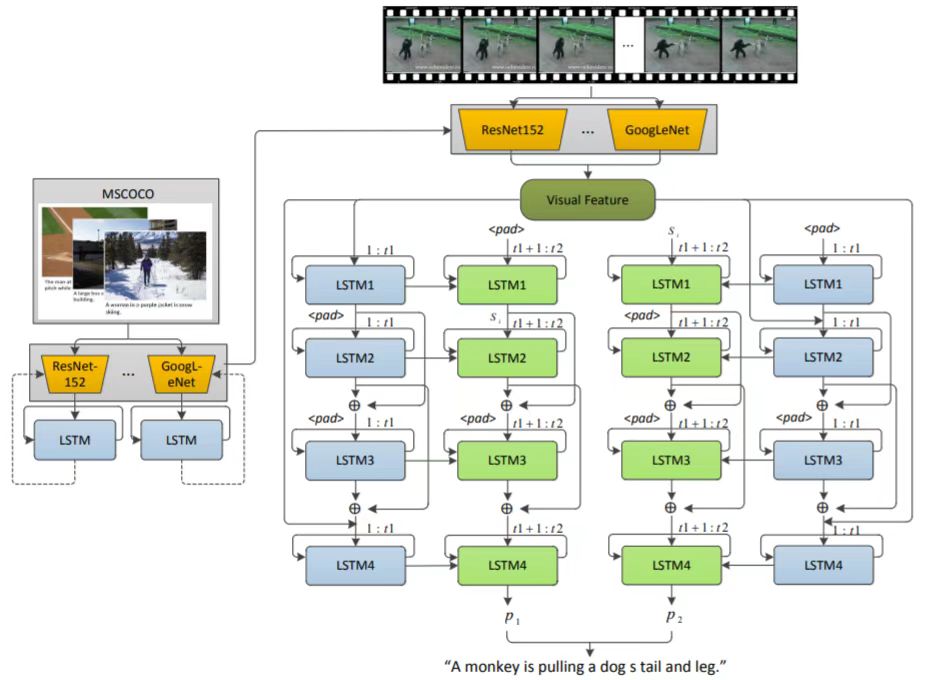
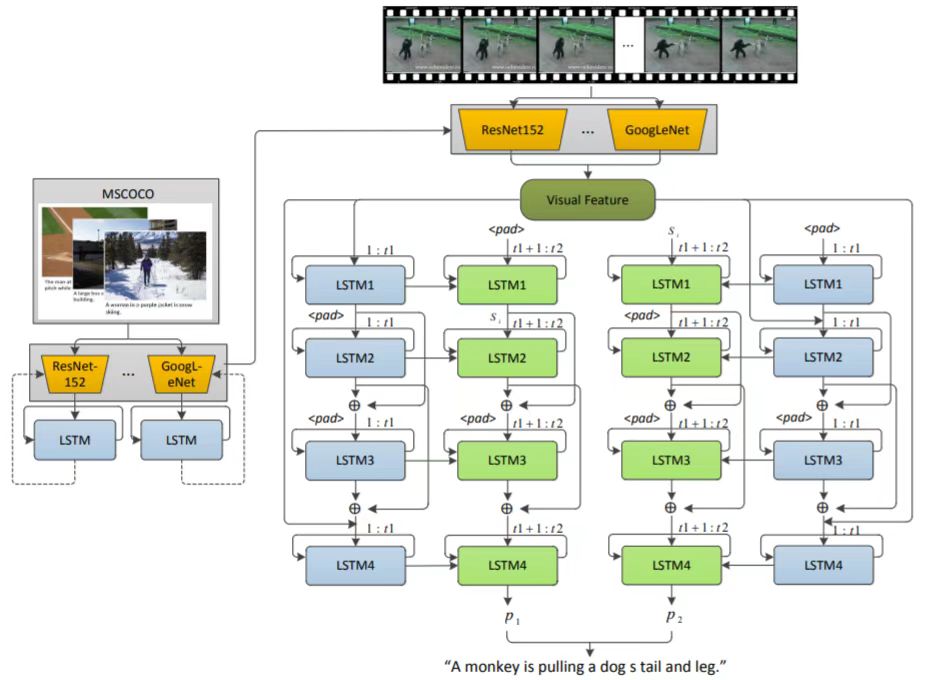
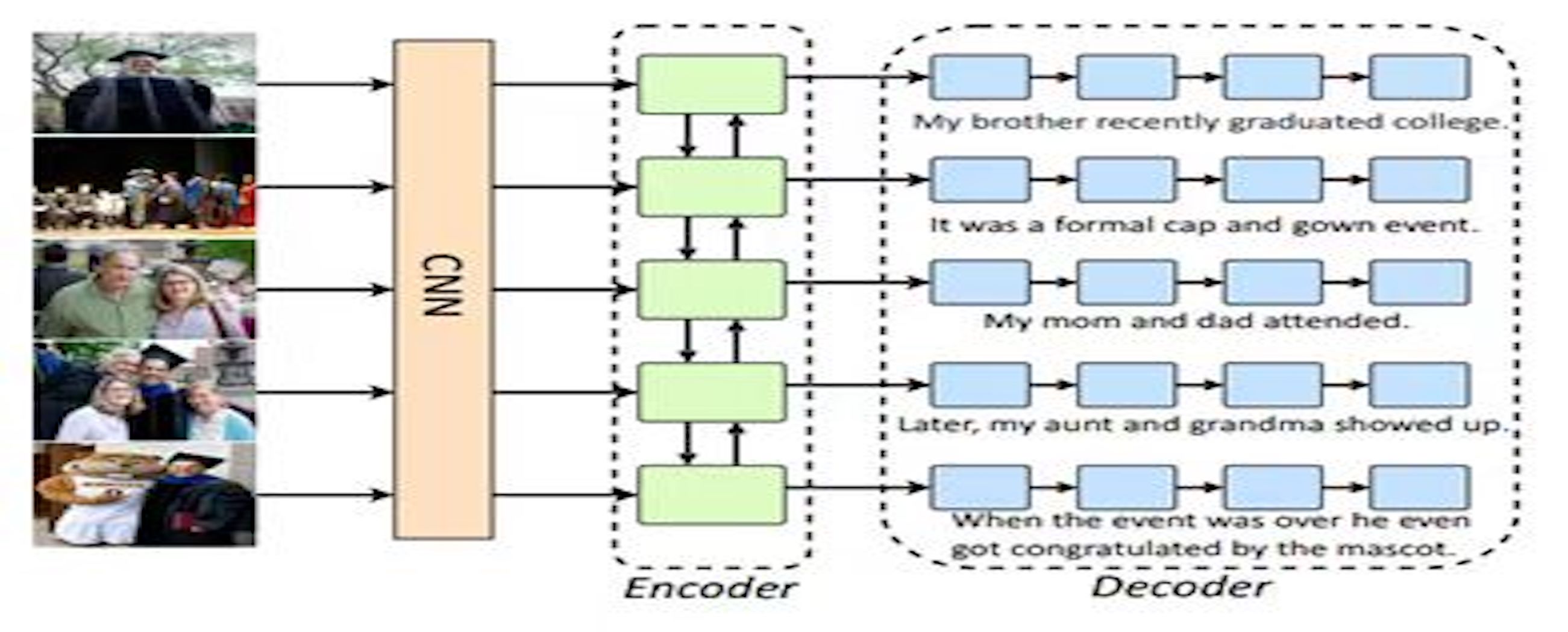
Multimedia and Intelligent Computing Lab (MIC)
Information Coding
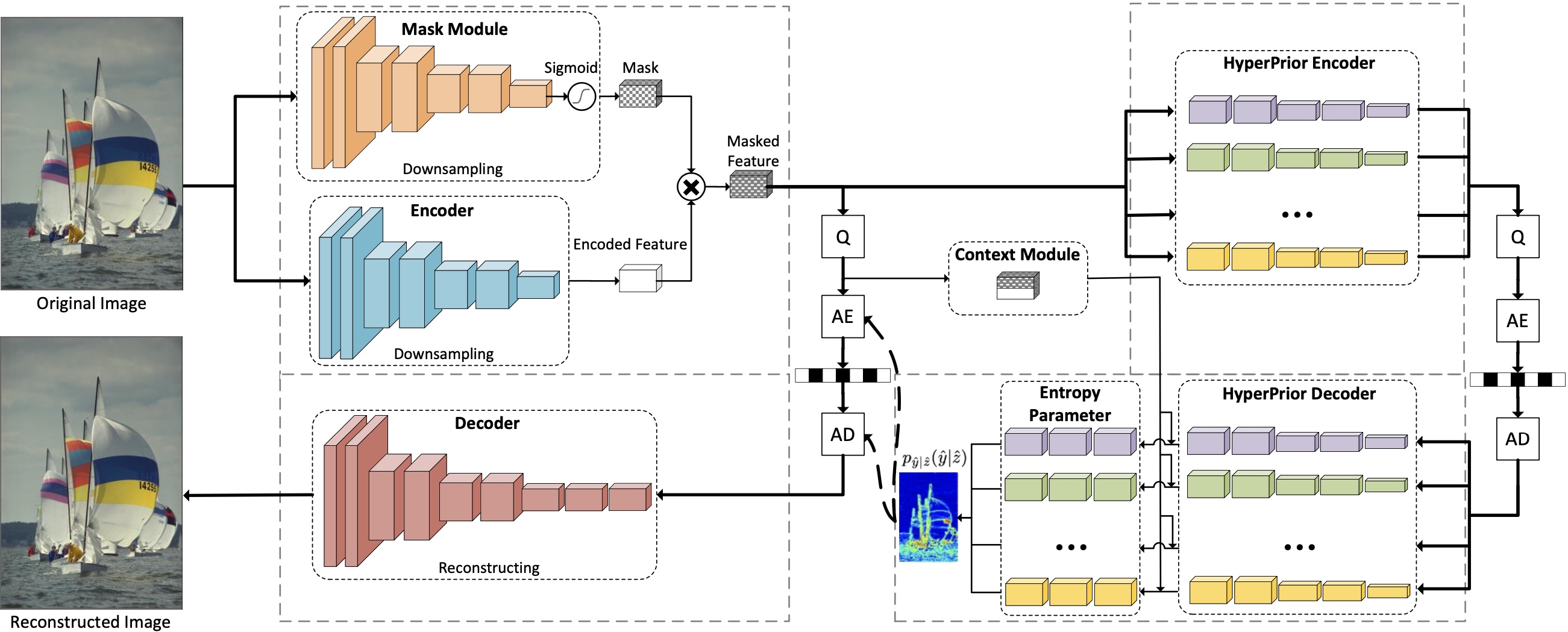
Information coding is a key technology in the field of multimedia computing and communication transmission. Its purpose is to eliminate all kinds of redundant information in visual signals, so as to store and transmit data in a more efficient way. The purpose of information coding for intelligent applications is no longer limited to saving storage space and transmission bandwidth, and providing users with high-definition visual services, but to provide efficient visual data representation for more intelligent visual analysis and processing needs.
Visual Question Answer
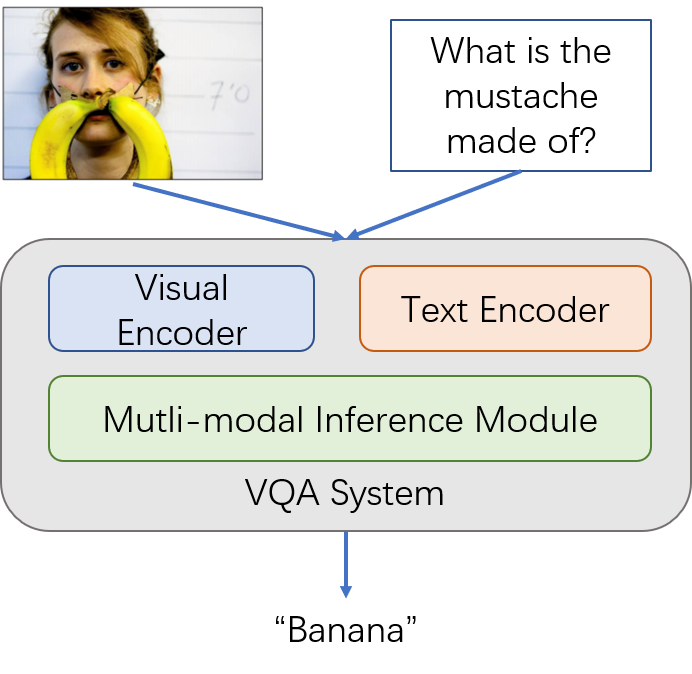
Visual question answering is a task in which a model answers human questions based on a given image. The challenge lies not only in the adequate understanding of images and texts, but also in the effective inference of the multimodal information obtained to complete complex question answers. Visual question-and-answer research has gained extensive attention in the fields of computer vision, natural language processing and multimedia analysis, and has great potential in visual disability assistance, intelligent education, online shopping guide, unmanned driving assistance and other scenarios.
Visual Dialog
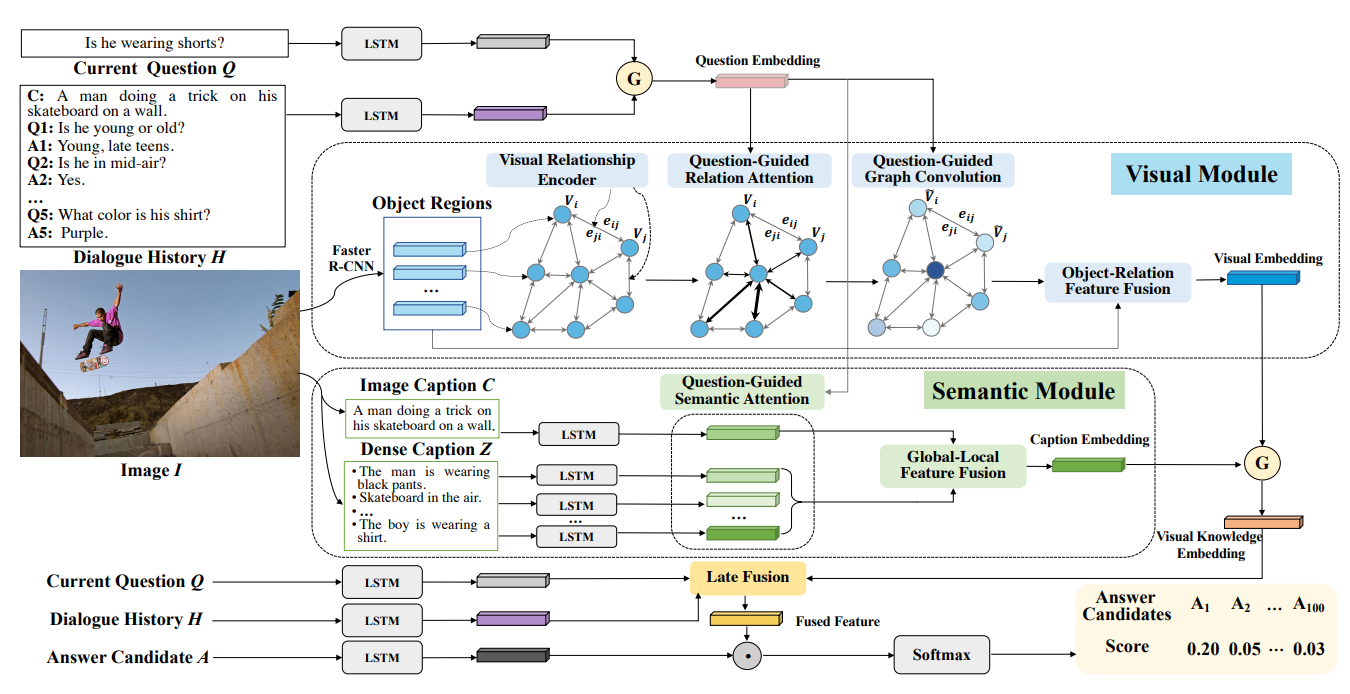
The visual dialog task requires an AI agent to interact with humans in multi-round dialogs based on a visual environment. The core challenges of this task is visual co-reference resolution and the effective inference of the multi-modal information. As a step towards conversational visual AI, visual dialog task can aid visually impaired users in understanding their surroundings or social media content, or aid analysts in making decisions based on large quantities of surveillance data, or interact with an AI assistant.
Visual Commonsense Reasoning
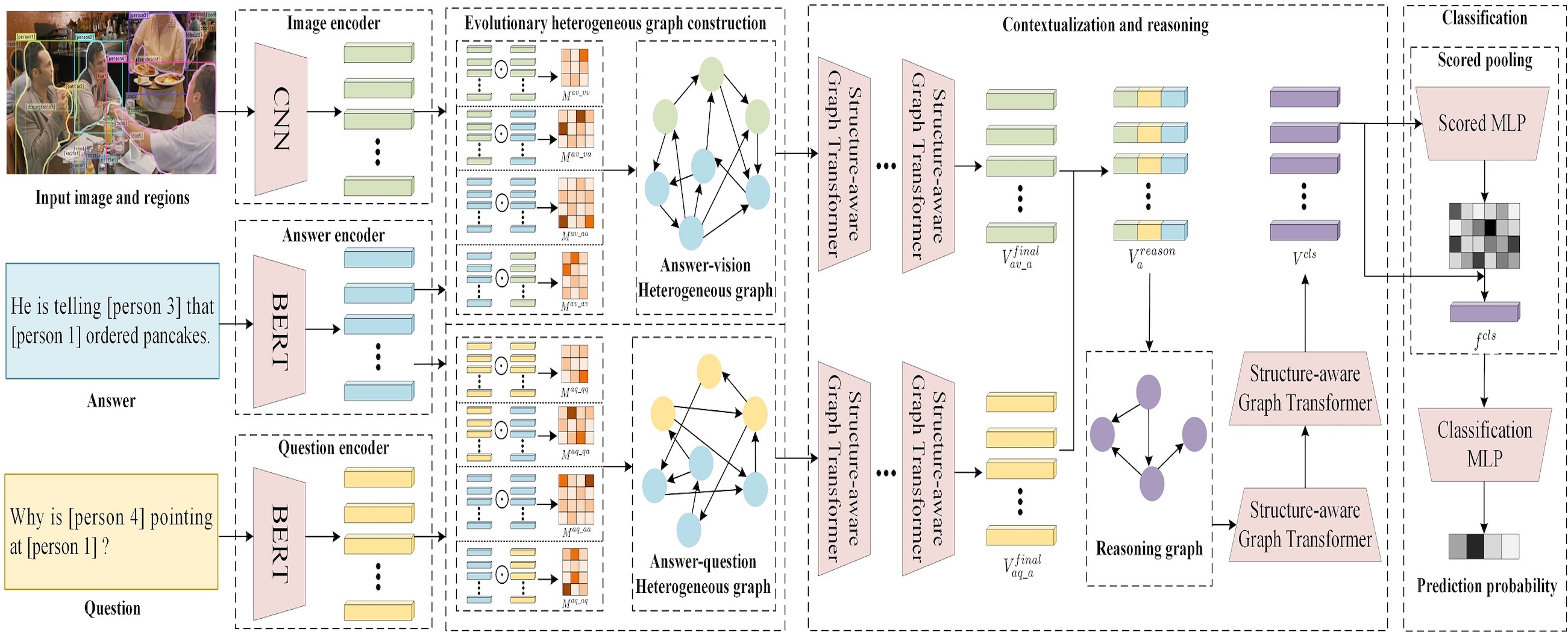
Given an image and a question, visual commonsense reasoning (VCR) is a task that contains two four-way multiple choice subtasks. The task needs not only answer the question, but also provides a rationale justifying for the choice. In addition, the choices in VCR are represented with more complex visual and linguistic expressions instead of simple short phrases. VCR as a cognition-level reasoning task has gain increasing attention from both academia and industry, which can be applied in many fields such as human-computer interaction, preschool education and visual disability assistance.
Image Restoration
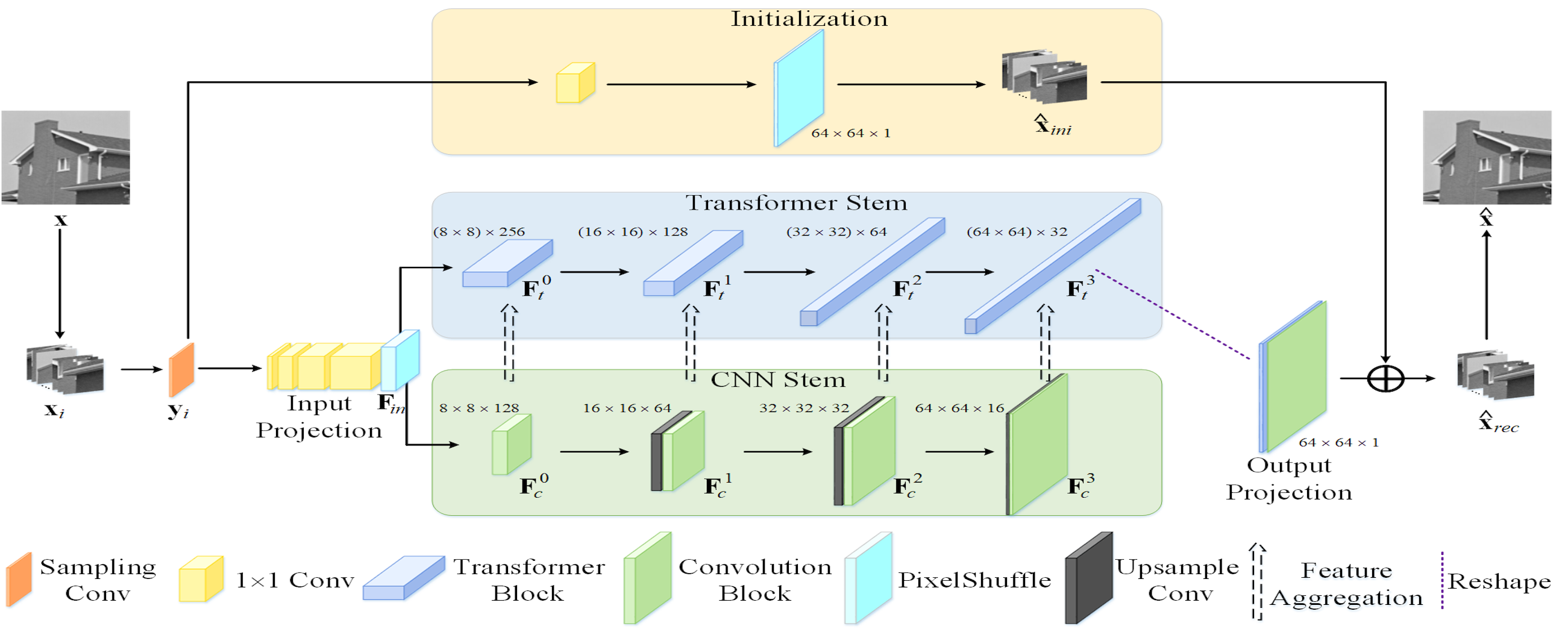
Image restoration is the process of recovering an image from a degraded version—degradations come from the image-capture process (e.g., noise, lens blur), post-processing (e.g., JPEG compression), or photography in non-ideal conditions (e.g., haze, motion blur), etc. It is a fundamental problem in image processing, but a highly ill-posed problem due to the existence of infinite feasible solutions. The image degradations not only impact human visibility, but also degrade various computer vision applications, such as autonomous driving, drone flying, and surveillance systems, etc. Therefore, it is crucial for image restoration to remove any unnecessary information while carefully preserving the desired content according to specific needs.
Image Enhancement
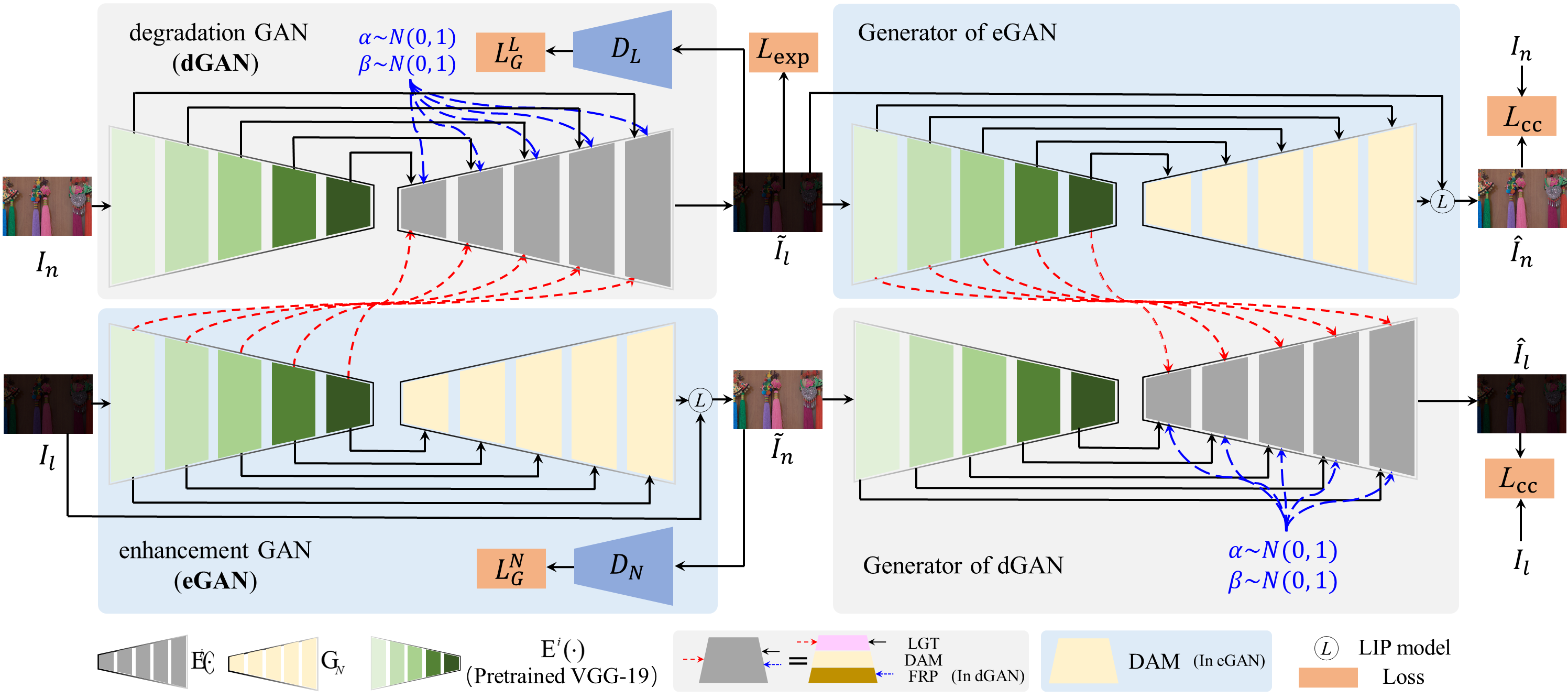
The principal objective of image enhancement is to process the information of a given image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application, such as improving visual quality for human beings or improving visual understanding for downstream high-level computer vision tasks. Image enhancement typically improves image quality via various post-processing techniques, such as contrast enhancement, color reproduction, and sharpening. Experienced photographers can freely generate their favorite visually pleasing images through professional image-editing software (e.g., Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom), which are desired by the general public who lacks professional image-editing skills. This contradiction highlights the importance of the user-oriented automatic image enhancement method for the general public to produce the high-quality images they want. Furthermore, automatic image enhancement is already a build-in technology for displays, cameras, scanners, and photography applications to provide users with better-customized services.
Image Quality Assessment
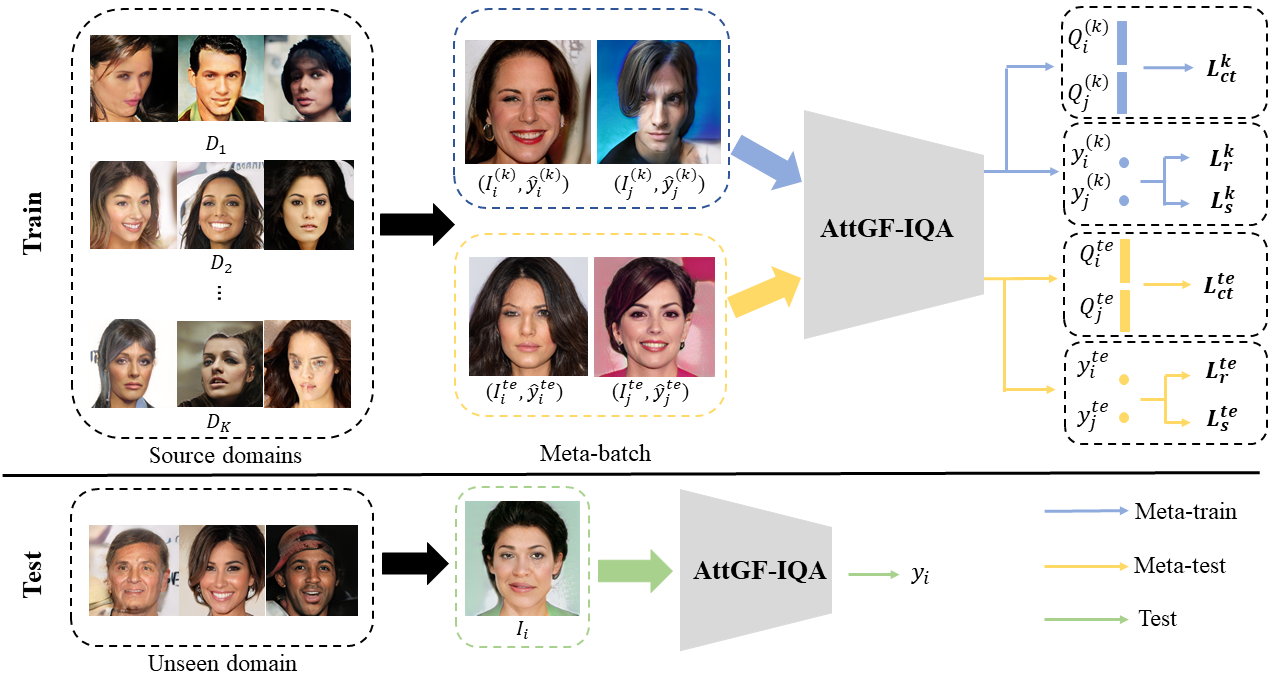
Image quality assessment (IQA) is a fundamental problem in both human and computational vision, and is critical in various real-world applications, such as image compression, image enhancement, image restoration, and so on. It has evolved rapidly in the past two decades and has also gained increasing attention from both academic and industry due to its wide range of applications. IQA can be divided into subjective IQA and objective IQA according to the subject of assessment. The goal of subjective IQA is to collect reliable mean opinion scores (MOS) from human subjects on the perceived quality of test images, which is the most straightforward and reliable method. Objective IQA aims to develop computational algorithms that automatically provide quality predictions consistent with human data. It is highly nontrivial to apply IQA techniques in the field of multimedia, and it continues to play a fundamental role in the development of signal and image processing algorithms.
Information Coding

Information coding is a key technology in the field of multimedia computing and communication transmission. Its purpose is to eliminate all kinds of redundant information in visual signals, so as to store and transmit data in a more efficient way. The purpose of information coding for intelligent applications is no longer limited to saving storage space and transmission bandwidth, and providing users with high-definition visual services, but to provide efficient visual data representation for more intelligent visual analysis and processing needs.
Visual Question Answer

Visual question answering is a task in which a model answers human questions based on a given image. The challenge lies not only in the adequate understanding of images and texts, but also in the effective inference of the multimodal information obtained to complete complex question answers. Visual question-and-answer research has gained extensive attention in the fields of computer vision, natural language processing and multimedia analysis, and has great potential in visual disability assistance, intelligent education, online shopping guide, unmanned driving assistance and other scenarios.
Visual Dialog

The visual dialog task requires an AI agent to interact with humans in multi-round dialogs based on a visual environment. The core challenges of this task is visual co-reference resolution and the effective inference of the multi-modal information. As a step towards conversational visual AI, visual dialog task can aid visually impaired users in understanding their surroundings or social media content, or aid analysts in making decisions based on large quantities of surveillance data, or interact with an AI assistant.
Visual Commonsense Reasoning

Given an image and a question, visual commonsense reasoning (VCR) is a task that contains two four-way multiple choice subtasks. The task needs not only answer the question, but also provides a rationale justifying for the choice. In addition, the choices in VCR are represented with more complex visual and linguistic expressions instead of simple short phrases. VCR as a cognition-level reasoning task has gain increasing attention from both academia and industry, which can be applied in many fields such as human-computer interaction, preschool education and visual disability assistance.
Image Restoration

Image restoration is the process of recovering an image from a degraded version—degradations come from the image-capture process (e.g., noise, lens blur), post-processing (e.g., JPEG compression), or photography in non-ideal conditions (e.g., haze, motion blur), etc. It is a fundamental problem in image processing, but a highly ill-posed problem due to the existence of infinite feasible solutions. The image degradations not only impact human visibility, but also degrade various computer vision applications, such as autonomous driving, drone flying, and surveillance systems, etc. Therefore, it is crucial for image restoration to remove any unnecessary information while carefully preserving the desired content according to specific needs.
Image Enhancement

The principal objective of image enhancement is to process the information of a given image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application, such as improving visual quality for human beings or improving visual understanding for downstream high-level computer vision tasks. Image enhancement typically improves image quality via various post-processing techniques, such as contrast enhancement, color reproduction, and sharpening. Experienced photographers can freely generate their favorite visually pleasing images through professional image-editing software (e.g., Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom), which are desired by the general public who lacks professional image-editing skills. This contradiction highlights the importance of the user-oriented automatic image enhancement method for the general public to produce the high-quality images they want. Furthermore, automatic image enhancement is already a build-in technology for displays, cameras, scanners, and photography applications to provide users with better-customized services.
Image Quality Assessment

Image quality assessment (IQA) is a fundamental problem in both human and computational vision, and is critical in various real-world applications, such as image compression, image enhancement, image restoration, and so on. It has evolved rapidly in the past two decades and has also gained increasing attention from both academic and industry due to its wide range of applications. IQA can be divided into subjective IQA and objective IQA according to the subject of assessment. The goal of subjective IQA is to collect reliable mean opinion scores (MOS) from human subjects on the perceived quality of test images, which is the most straightforward and reliable method. Objective IQA aims to develop computational algorithms that automatically provide quality predictions consistent with human data. It is highly nontrivial to apply IQA techniques in the field of multimedia, and it continues to play a fundamental role in the development of signal and image processing algorithms.