Perceptually Weighted Mean Squared Error Based Rate-Distortion Optimization for HEVC
Xiuzhe Wu, Hanli Wang, Sudeng Hu, Sam Kwong, and C.-C. Jay Kuo
Overview:
The process of rate-distortion (RD) optimization plays a key role for video coding, which aims to achieve a tradeoff between compression efficiency and video quality distortion. Although the conventional objective distortion metric mean squared error (MSE) performs well in computational complexity, it is not always in accordance with the perceptual quality perceived by human visual system (HVS). Taking the characteristics of HVS into consideration, a perceptually weighted mean squared error (PWMSE) based RD model is proposed in this work. The main contributions of this work include the following two aspects: (1) PWMSE is recast in both the spatial and temporal domain in order to be calculated within each coding unit instead of an entire image/video, and (2) the refined coding unit based PWMSE is employed as the distortion metric and a novel rate-distortion optimization (RDO) model is accordingly designed for HEVC encoding.
Method:
First, a low-pass filter is employed to process the original distortion information in order to simulate visual signal processing and obtain the perceptual distortion. Then, masking modulation in both temporal and spatial domains is introduced into distortion model, and a novel Lagrange multiplier is derived accordingly. Finally, the proposed PWMSE based RD model is applied to the high efficiency video coding standard.
Results:
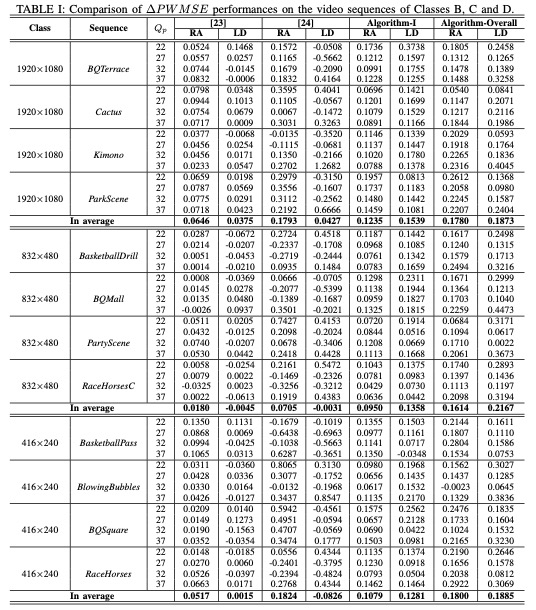
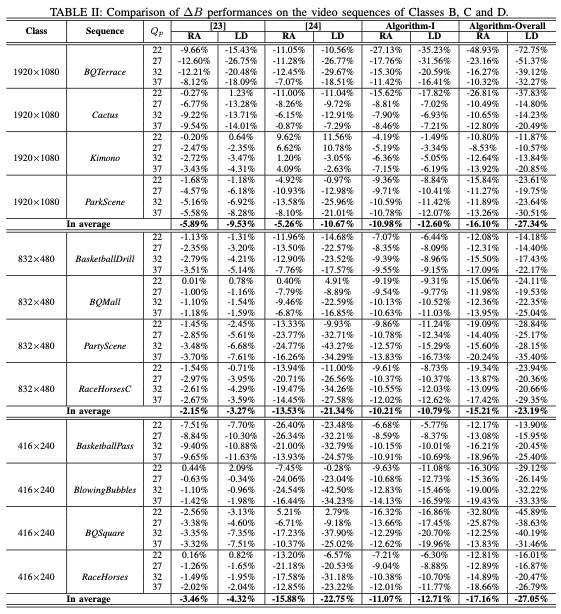
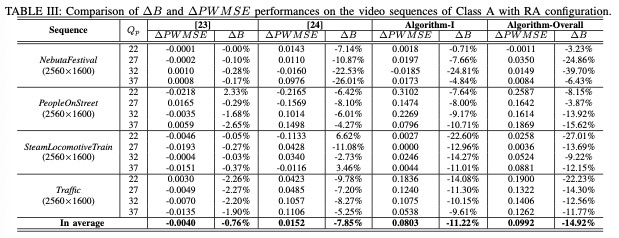
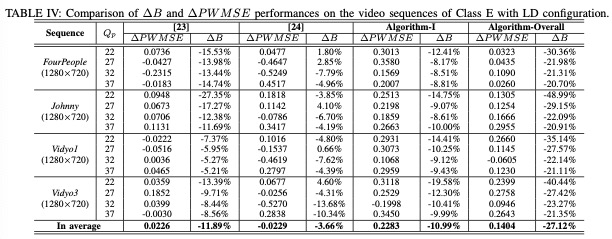
Two algorithms are defined in the following experiments, including Algorithm-I and Algorithm-Overall. Specifically speaking, Algorithm-I only applies the first step of our proposed RD model and Algorithm-Overall stands for the overall algorithm. Moreover, two state-of-the-art algorithms [23] and [24] are employed for performance comparison.
In total, there are twenty HEVC benchmark video sequences employed for performance evaluation, which can be divided into five classes with five kinds of resolution (Class A: 2560x1600, Class B: 1920x1080, Class C: 832x480, Class D: 416x240, and Class E: 1280x720). The video sequences from Classes A, B, C and D are tested with the random access (RA) configuration while the video sequences from Classes B, C, D and E are tested with the low delay (LD) configuration. Four Qp values including 22, 27, 32 and 37 are applied to generate the target bitrate of the anchor HEVC encoder, and all the frames of each test sequence are coded.
The results are shown in Table I-Table IV. The performances of these competing methods are evaluated from two aspects: compression efficiency and perceived quality. ΔB is bit saving and ΔPWMSE denotes PWMSE improvement.
Source Code:
Citation:
Please cite the following paper if you find this work useful:
X. Wu, H. Wang, S. Hu, S. Kwong, and C.-C. J. Kuo, Perceptually Weighted Mean Squared Error Based Rate-Distortion Optimization for HEVC, IEEE Trans. Broadcast., vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 824-834, Dec. 2020.
References:
[23] S. Li, C. Zhu, Y. Gao, Y. Zhou, F. Dufaux, and M. T. Sun, "Lagrangian multiplier adaptation for rate-distortion optimization with inter-frame dependency," IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 117–129, Jan. 2016.
[24] S. Wang, A. Rehman, Z. Wang, S. Ma, and W. Gao, "Perceptual video coding based on SSIM-inspired divisive normalization," IEEE Trans. Image Processing, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 1418–1429, Apr. 2013.
