Knowledge-enriched Attention Network with Group-wise Semantic for Visual Storytelling
Tengpeng Li, Hanli Wang, Bin He, Chang Wen Chen
Overview:
As a technically challenging topic, visual storytelling aims at generating an imaginary and coherent story with narrative multi-sentences from a group of relevant images. Existing methods often generate direct and rigid descriptions of apparent image-based contents, because they are not capable of exploring implicit information beyond images. Hence, these schemes could not capture consistent dependencies from holistic representation, impairing the generation of a reasonable and fluent story. To address these problems, a novel knowledge-enriched attention network with group-wise semantic model is proposed. Specifically, a knowledge-enriched attention network is designed to extract implicit concepts from external knowledge system, and these concepts are followed by a cascade cross-modal attention mechanism to characterize imaginative and concrete representations. Then, a group-wise semantic module with second-order pooling is developed to explore the globally consistent guidance. Finally, a unified one-stage story generation model with encoder-decoder structure is proposed to simultaneously train and infer the knowledge-enriched attention network, group-wise semantic module and multi-modal story generation decoder in an end-to-end fashion. Substantial experiments on the visual storytelling datasets with both objective and subjective evaluation metrics demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed scheme as compared with other state-of-the-art methods.
Method:
As shown in Fig. 1, the proposed KAGS is one-stage encoder-decoder structure, with the designed knowledge-enriched attention network, group-wise semantic module and multi-modal story generation decoder. Specifically, a Faster-RCNN network and a ResNet backbone are used to extract regional features and high-level convolutional features.Then, the proposed knowledge-enriched attention network (KAN) is designed to leverage the external knowledge and visual information to characterize the cross-modal interactions with attention mechanism. Moreover, the group-wise semantic module (GSM) is devised to explore the group-wise semantic with second-order pooling to obtain the storyline with global feature guidance. Finally, all these extracted multi-modal representations are then fed into the decoder for story generation.

Fig. 1. Overview of the proposed KAGS framework.
The self-attention (SA) and cross-attention (CA) units are shown in Fig. 2. To selectively enhance the fine-grained visual and cross-modal representations, X-Linear attention block is applied to SA and CA units, followed by a point-wise addition, a linear layer and a BatchNorm layer.
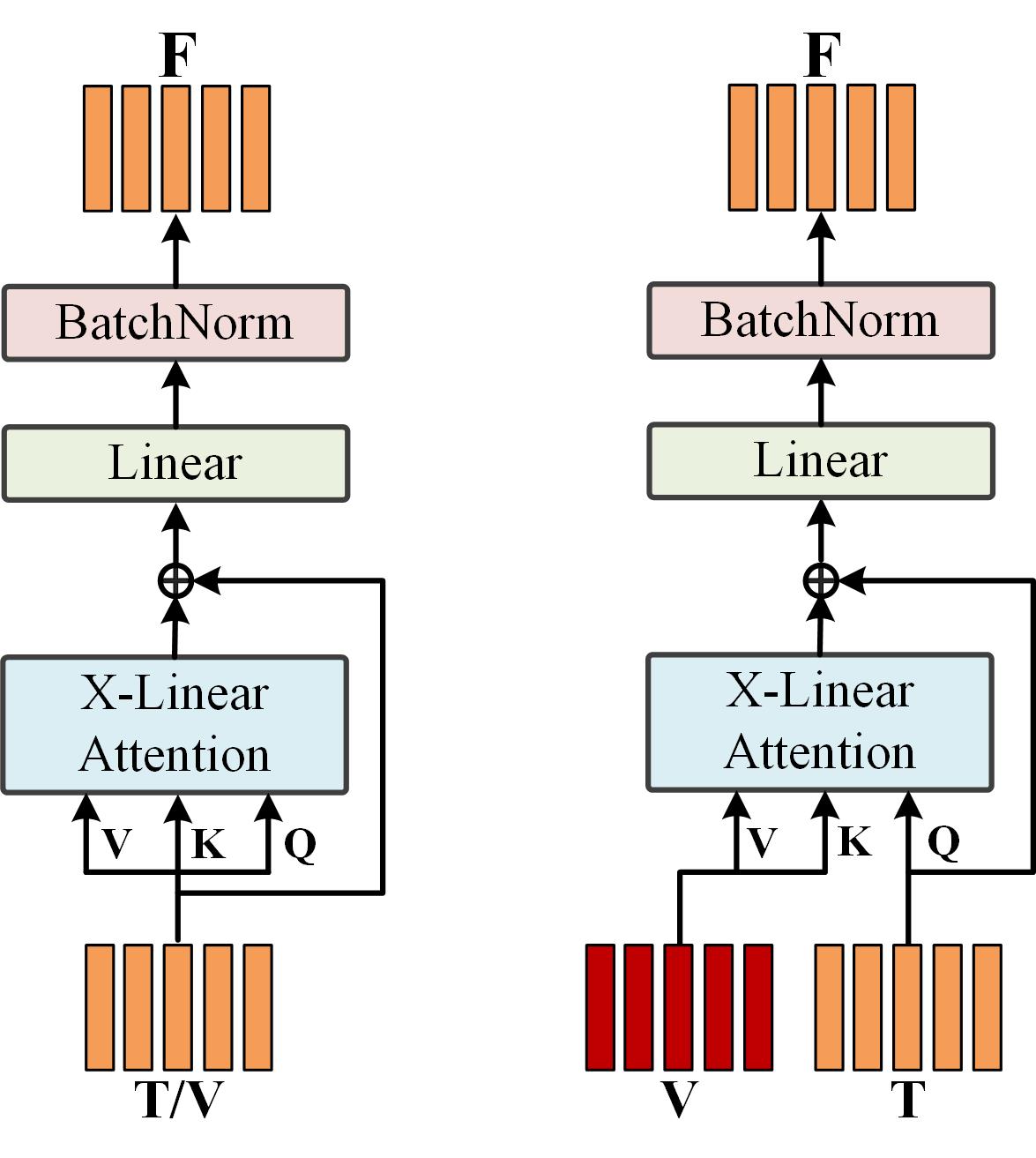
Fig. 2. Illustration of the self-attention and cross-attention units.
The structure of second-order pooling (SOP) is shown in Fig. 3, given an input feature tensor with size , it is fed into SOP, which consists of two convolutions, one transpose multiplication operator and one row-wise convolution, generating a global guided aggregation.
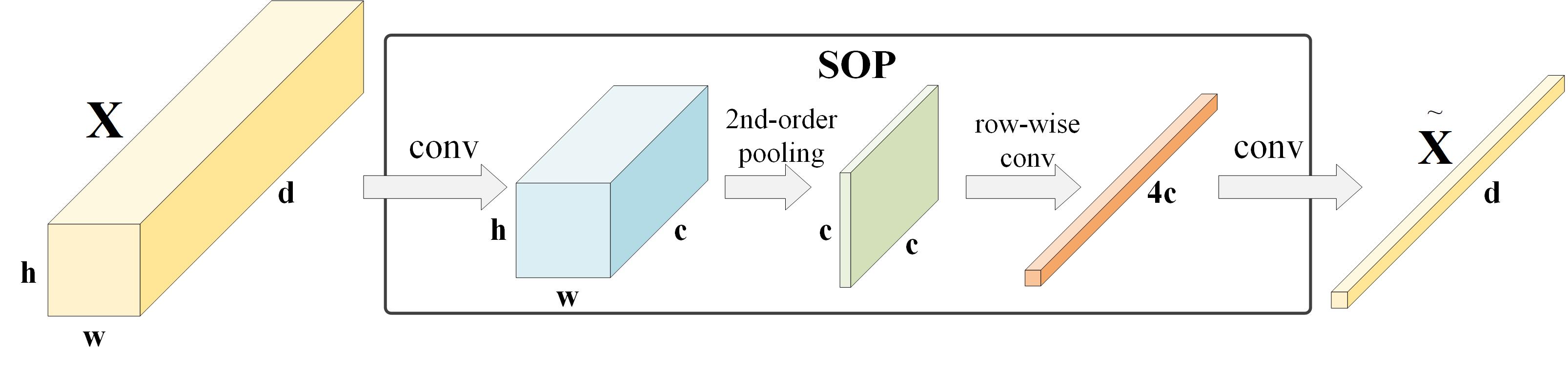
Fig. 3. Illustration of second-order pooling.
Results:
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, KAGS is compared with other thirteen state-of-the-art visual storytelling approaches on VIST and LSMDC datasets. The statistical results are shown in Table1. To further reflect the semantic properties of many stories (e.g., coherence and expressiveness), the human evaluation is conducted and the results are presented in Table2. Moreover, figure 4 presents several visual comparisons between the proposed KAGS model and the methods AREL and VSCMR, together with the human-annotated referenced stories (GT).
Table1. Comparisons of proposed method with other state-of-the-art approaches on the VIST and LSMDC datasets, where the bold font indicates the best performance.
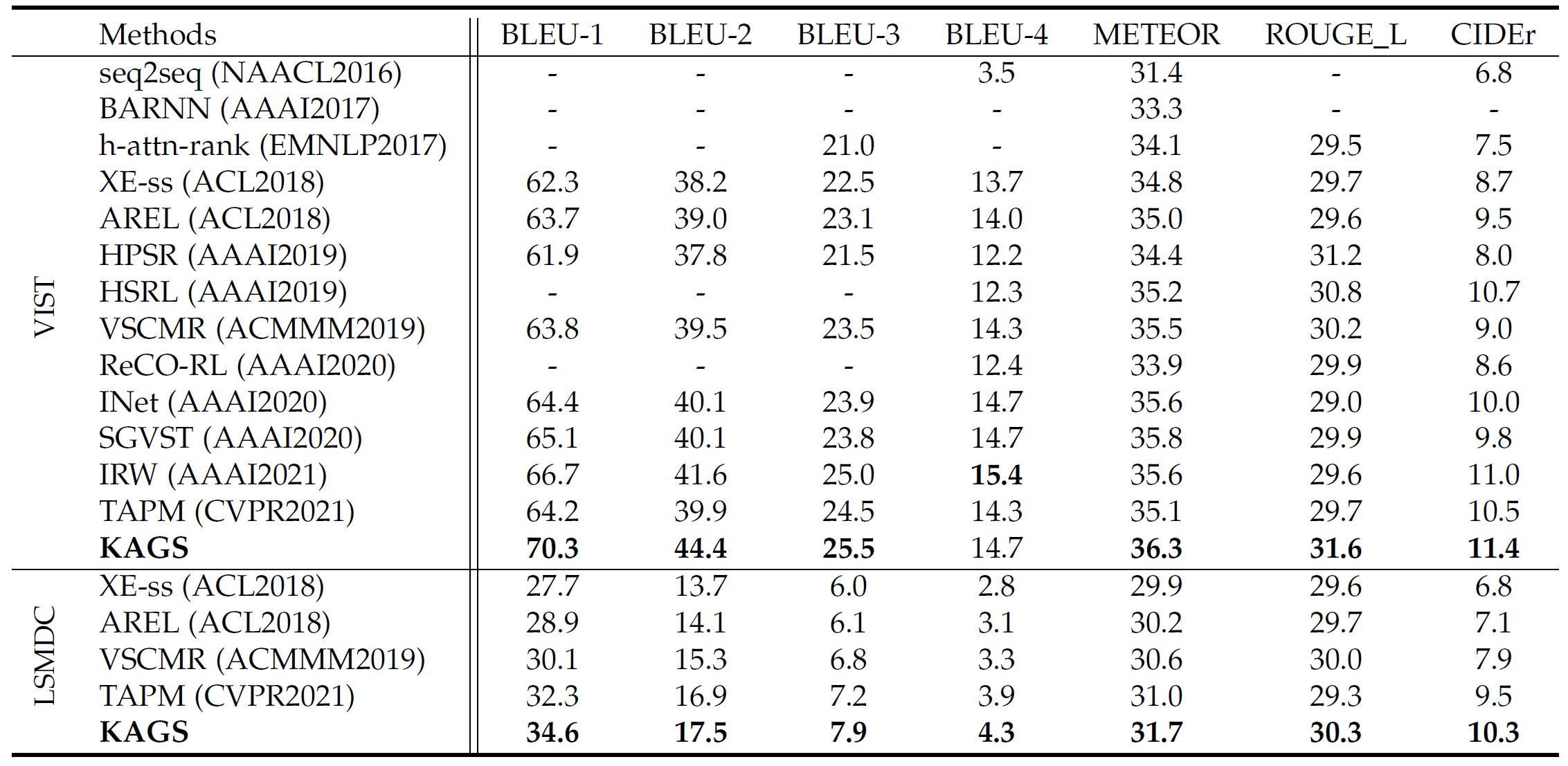
Table2. Statistical results of human evaluation metrics on VIST, here the percentage numbers represent the confident scores of the tester believe that a model surpasses its opponent, and Tie means the tester can not choose the better story.
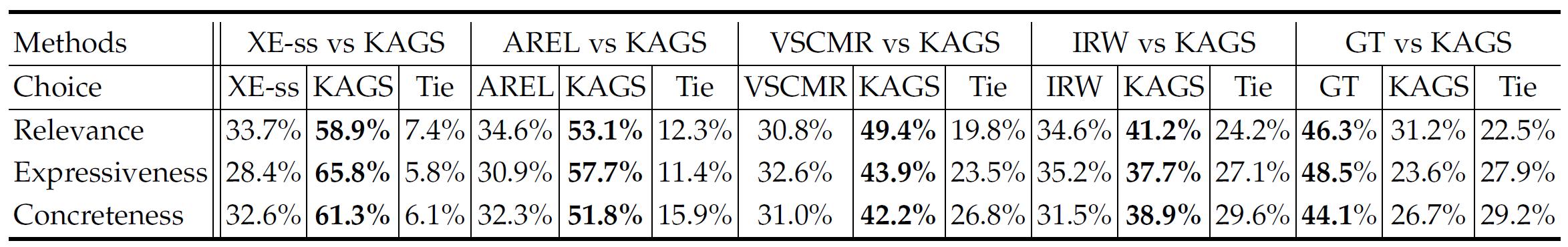
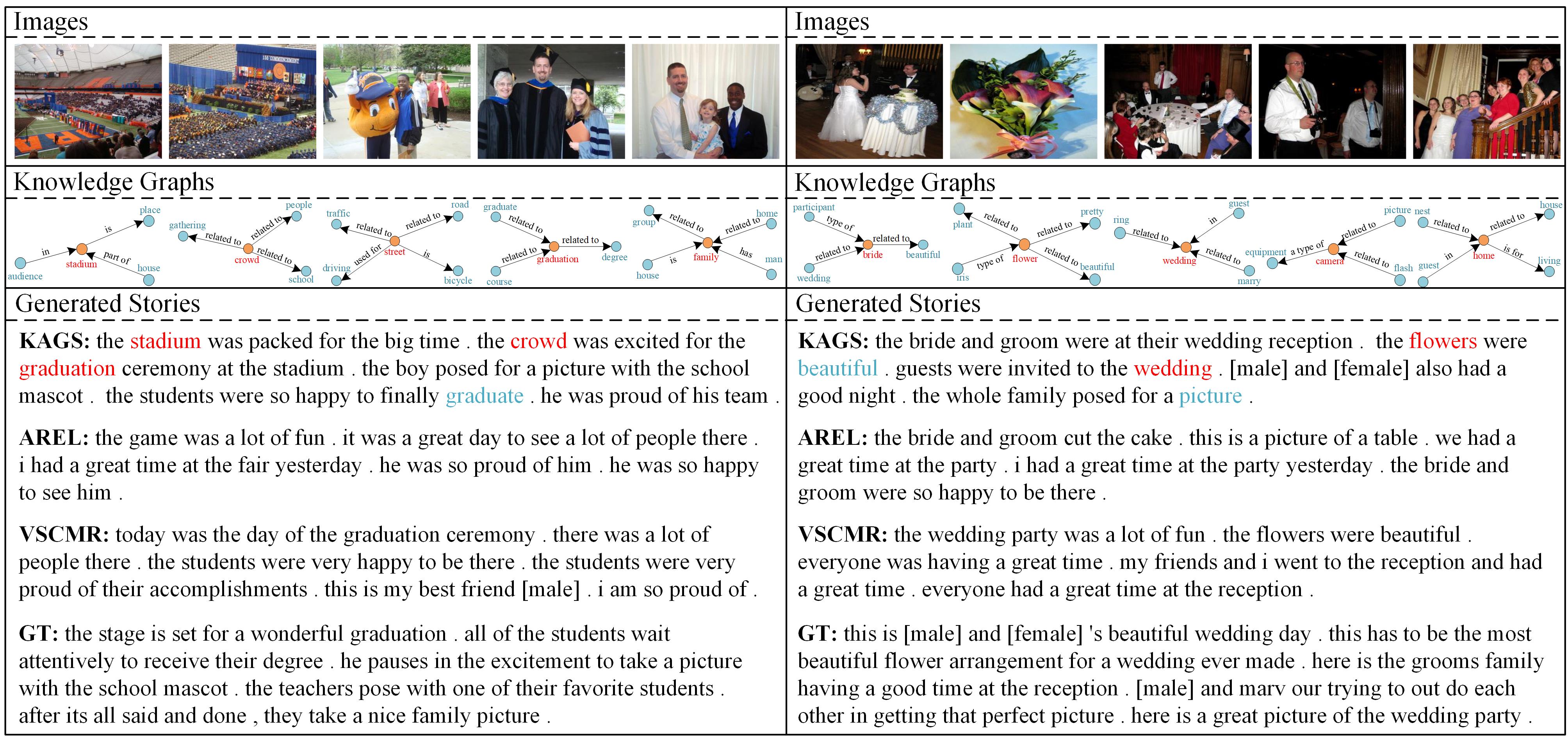
Fig. 4. Visualization of the comparison between the proposed KAGS and other state-of-the-art methods including AREL, VSCMR and ground-truth on the VIST dataset. Only parts of the extracted commonsense knowledge graphs are visualized due to the space limit, where the words highlighted in red and blue represent the semantic seeds and commonsense words, respectively.
Source Code:
Citation:
Please cite the following paper if you find this work useful:
Tengpeng Li, Hanli Wang, Bin He, and Chang Wen Chen, Knowledge-enriched Attention Network with Group-wise Semantic for Visual Storytelling, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 45, no. 7, pp. 8634-8645, Jul. 2023, DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3230934.
