Richer Feature for Image Classification with Super and Sub Kernels Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Pengjie Tang, Hanli Wang
Department of Computer Science and Technology, Tongji University, Shanghai, P. R. China
Abstract:
The deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) has obtained great success for image classification. However, the principle of human visual system (HVS) is not fully investigated and incorporated into current popular DCNN models. In this work, a novel DCNN model named parallel crossing DCNN (PC-DCNN) is designed to simulate HVS. In addition, the concepts of super convolutional kernel and sub convolutional kernel are introduced to sumulate the process of human vision. Afterwards, a multi scale PC-DCNN (MS-PC-DCNN) framework is designed, with which a batch of PC-DCNN models are deployed and the scores from each PC-DCNN model are fused by weighted average for final prediction. Experimental results on four public datasets verify the superiority of the proposed method as compared to a number of state-of-the-art models.
Overview:
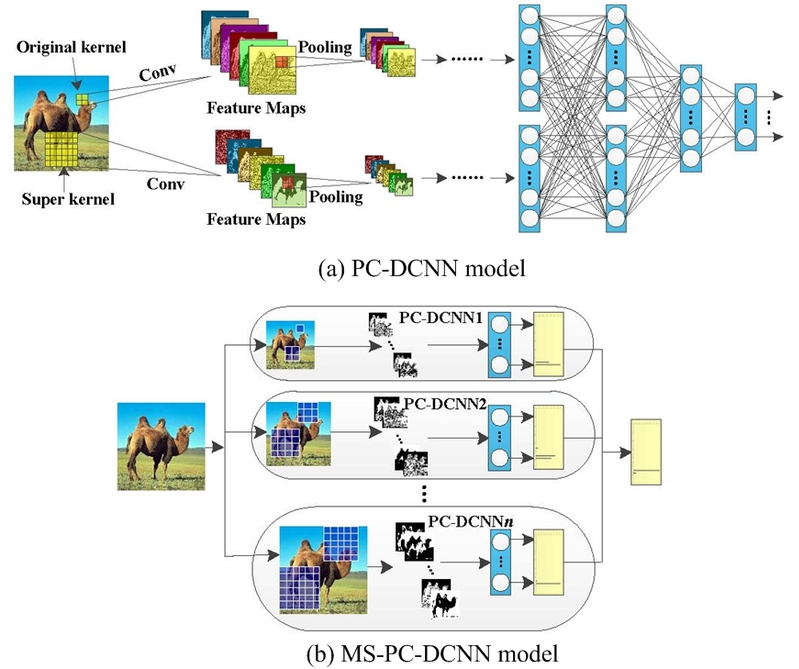
Fig. 1 Overview of the proposed PC-DCNN and MS-PC-DCNN models
As we know, the visual information goes into the brain through two visual pathways, and then it comes into being more comprehensive information via the optic chiasma. The comprehensive information at last is more discriminative and abstract. Therefore, in this work, we simulate human eyes with two types of convolutional kernels with different sizes at the bottom layer; and then, the extracted information forms two streams and is forwarded via each other's pathway. When the features arrive at the top of the proposed model, these two streams will be fused, which is similar to the mechanism of optic chiasma. According to this process, we design a novel architecture called parallel crossing DCNN (PC-DCNN) as shown in Fig. 1(a)
Actually, the ability of human eyes is limited, and most often people have to turn to some optical equipments for more information about the objects they want to understand or recognize. For example, people use telescope for observing the macro features of objects, and they use microscope for getting the information of microstructure. The more information about the objects can be used, the higher precision can be obtained. We simulate this process by multi-scale convolutional kernels and develop the multi-scale PC-DCNN (MS-PC-DCNN) model as shown in Fig. 1(b). In MS-PC-DCNN, we use super convolutional kernel to simulate the process of using telescopes, and employ sub convolutional kernel to simulate the process of using microscopes. By this way, a batch of trained DCNN models and a few groups of scores are obtained, then, we fuse all the models' scores by computing their weighted average. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed models can improve the performance greatly for image classification. Meanwhile, the proposed framework is expandable, so if we employ more and smaller sub convolutional kernels, more PC-DCNN modules can be generated, and the performance can be further improved.
Performances:

Fig. 2 Performance comparison of the proposed MS-PC-DCNN model with different multi scales
We employ the popular Caffe toolkit to deploy and implement the proposed models. For images with large size, we use the Caltech101 and Caltech256 datasets for evaluating our approach. And for the tiny image, we use the popular CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets for evaluation.
The results are shown in Fig. 2, where it is obvious that the performances are improved by increasing the number of PC-DCNN modules. Especially on Caltech256 and Caltech101, the 4-Scale model achieves the accuracy of 54.4% and 72.6%, respectively, outperforming the original PC-DCNN model more than 7% and 6%, respectively. On the CIFAR-100 dataset, the 4-scale model obtains the test error which outperforms the original PC-DCNN with 6.01%. Even on the CIFAR-10 dataset, the 4-scale model reduces the test error about 1.7% as compared to the original PC-DCNN model.
Source Code:
MS-PC-DCNN-1.0: ![]() MS-PC-DCNN-1.0.tar.gz
MS-PC-DCNN-1.0.tar.gz
Citation:
Please cite the following paper when using our proposed MS-PC-DCNN.
Pengjie Tang and Hanli Wang, Richer Feature for Image Classification with Super and Sub Kernels Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network, Computers and Electrical Engineering, vol. 62, pp. 499-510, Aug. 2017, DOI: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.01.011.
